is defined as the quantity of a product or commodity, which a producer is willing and able to make available for sale at any given price during some specified period of time. Supply is not the same thing as the total stock of the commodity in existence. But it is the part of a portion of total stock, which is offered for sale at a ruling price.
In supply, we have individual and market supply just as it exist in the demand theory. Individual supply is the amount of quantity of a product, which a supplier is willing and able to supply or make available for sale at any given price and at a particular time. While market supply on the other hand, is the total amount of a product which all the suppliers in the market are willing and able to make available for sale at any given price and at a particular time.
SUPPLY SCHEDULE
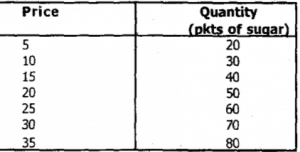
This is a table that shows the quantity of goods supplied at various prices.
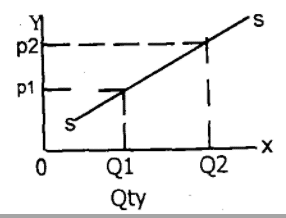
The above table shows that at the price of N5 a packet, 20 packets of sugar were supplied, but at N35 per packet, 80 packets were offered for sale, showing that the higher the price, the more the quantity to be supplied (law of supply). If the above table is represented in a graph, the supply curve will slope upward from left to right.
LAW OF SUPPLY:
This law states that the higher the price of a commodity, the higher the quantity producers or suppliers are willing to offer for sale.
FACTORS AFFECTING SUPPLY
- The price of the commodity
- Effects of the weather
- Effects of taxation
- Changes in technique of production
- Changes in the cost of production
- The tastes or goals of producers
- Prices of other commodity
- Natural influence – i.e. attack of pest on Agricultural products.
- Political situation.
- Government policy – i.e. Ban on some goods
TYPES OF SUPPLY
- Joint Supply: This is a situation in which two or more commodities are jointly supplied E.g. beef and leather, mutton and wool.
- Composite supply: This is a situation in which a group of commodities are supplied to satisfy a single demand E.g Tea, Coffee, Milk, and Sugar etc.
- Competitive Supply: This explains the goods that are competitively supplied. The supply of one commodity affect the supply of another commodity.