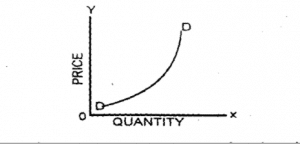
From the definition of demand, the normal demand curve slopes downward from left to right i.e. obeying the law of demand. But exceptional demand curve takes the opposite direction. It is a situation where less quantity of goods will be demanded even when there is a fall in price and, more quantity of goods demanded at even a higher price.
These conditions or situations may be found in the following commodities.
ARTICLES OF OSTENTATION
This is a situation where? the high price of goods is taken by consumers as being an indication for high quality. And when the prices of such goods or products curve are low, they (consumers) consider the products as being interior. An example can be taken in lase materials and the common wrapper. Also, a consumer may demand for goods at a higher price to show his statues quo i.e. v-boot cars, Mercedes Benz which are now en-vogue.
COMMODITIES WHOSE PRICE ARE EXPECTED TO RISE
This is a situation whereby consumers anticipates that the price of a commodity is likely to rise in future than at present. In view of this, goods are bought even if the price of such commodities is high. The situation is apparent in the stock exchange speculation where a rise in the price of shares is a signal to further rise in price.
INFERIOR GOODS
These are referred to as cheap and basic goods of necessity. E.g. food stuffs like cassava (akpu), garri, beans and rice. A fall in the prices still does not guarantee a high demand, even as the demand for the goods falls, the price of the goods still goes down more.
EXPECTATION OF FURTHER FALL IN PRICES
This situation arises when consumers expect a further fall in the price of a commodity and as such less of such commodities are demanded even at a lower price.