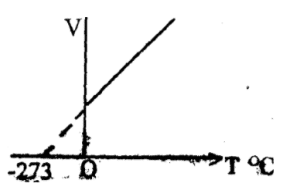
Charle’s law states that for a given mass of gas, the volume is directly proportional to the temperature at constant pressure.
V ∝ T
V = KT
K = V/T
V1/T1 = V2/T2
Remember: K° = C° + 273°
Example: A given mass of gas occupies a volume of 50cm3 at a temperature of 27°c. At what temperature will the volume occupied be 100mᶟ?
Solution
V1/T1 = V2/T2
V1 = 50mᶟ, T = 27°C = 27 + 273 = 300°K, V2 = 100mᶟ
T2 = (V2T1)/V2
= (100 x 300)/50
= 60°K
The new temperature is 60 °K