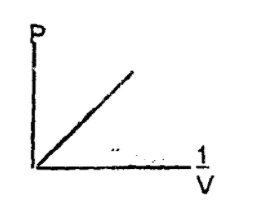
Boyle’s law states that for a given mass of gas, that the volume is inversely proportional to its pressure provided the temperature is constant.
V ∝ 1/P
K = PV
ie. V = K/P
P1V1 = P2Vsub>2
Example:
A given mass of gas of pressure 120 N/M2 occupies a volume of 30cm3. What will be the pressure exerted when the volume rises to 90cm3.
Solution:
P1V1 = P2Vsub>2
P1 = 120N/M2, V1 = 30cm3, P2 =? V2 = 90cm3
∴ P2 = (P1 V1)/V = (120 x 30)/90
= 40N/M2